Green fruitworm
Damage caused by the Green fruitworm
Only larval stages of green fruitworm cause damage to leaves and fruits of many plant species including apple, peach and cherry. Newly hatched larvae of green fruitworms generally feed on the leaves, buds, blooms and small fruits. Damaged fruits show sunken pits on their surface and they fall off trees prematurely. Damaged fruits that remain on trees until harvest also shows sunken and corky injuries. Mature larvae can burrow anterior end into fruits and feed on its content. In case of severe infestation, larvae of green fruit can completely defoliate their host plants.
Facts (show all)
- Common names
-
- Green fruitworm
- Scientific name
-
- Lithophane antennata
- Identification
-
Adults: Adults of the green fruitworms are gray in color with orbicular spots on the mottled forewings.
Eggs: Eggs of green fruitworm are reddish brown to grayish white in color.
Larvae/Caterpillars: Larvae of green fruitworms turn from cream to yellow to green in color as they become mature. Mature larvae are about 1 inch long with several white and yellow bands running longitudinally along their backs.
Pupae: Pupae of green fruitworm are dark reddish brown in color and about 1 inch long.
- Biology
-
Green fruitworms overwinter as adults on the ground. Early in the spring, adults move from their overwintering sites to blooming trees. After mating, females lay eggs on the bark of young branches and near to leaf buds. Eggs start hatching into first stage larvae when fruit buds start to grow. Hatched young larvae then start feeding on the leaves, buds and small fruits until they become mature. Mature larvae then pupate in the soil and life cycle continues. Green fruitworms generally complete one generation in a year.
- Organic Control of the Green fruitworm
-
- Following beneficial bugs and plant products are used for organic control of the Green fruitworm
- Egg parasitic wasps
-
- Trichogramma brassicae
- Trichogramma pretiosum
- Trichogramma minutum
- Trichogramma platneri
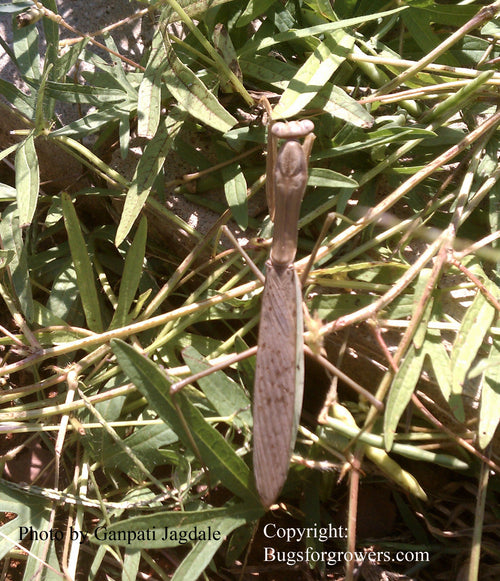
- Predatory praying mantis
-
- Tenodera aridifolia sinensis
- Stagmomantis crolina
- Plant Product
-
- Molt-X® - (Active ingredient – Azadirachtin a compound isolated from neem leaves)